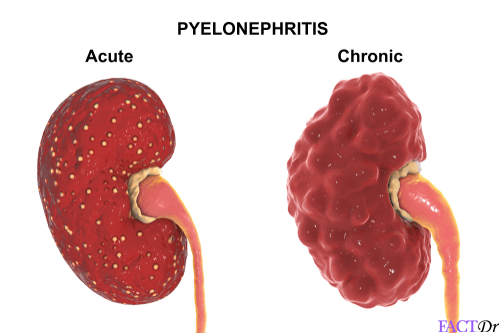
Symptoms of pyelonephritis include fever, nausea, vomiting, chills, abdominal pain, and the urge to urinate frequently. Patients may also have blood in their urine. A bacterial culture of the urine can determine the type of bacteria responsible for the infection. Pyelonephritis can lead to the development of chronic kidney disease if left untreated.
Acute pyelonephritis, which affects both adults and children, is a serious bacterial infection of the kidneys. It is caused by bacteria such as Escherichia coli, which enters the urinary system through the urethra. Once in the urinary tract, these bacteria multiply and begin to infect other parts of the kidney. Symptoms are usually characterized by a fever and pain, but they can also involve diarrhoea, hesitancy, and lower abdominal pain.
Symptoms may also include a burning sensation when urinating. If the infection is severe, it may require hospitalization. In hospitalization, IV fluids may be administered to control the infection. If the infection is causing laboured breathing or listlessness, the patient may be given antibiotics to prevent complications. In addition, supportive care may be provided to help with the symptoms.
If the infection is not severe, the patient may be able to treat the infection at home. Some common home treatments for urinary tract infections include bed rest and taking painkillers to ease pain. If antibiotics do not help, the doctor may recommend an ultrasound or MRI to help identify the cause of the infection. The doctor may also send blood cultures to the laboratory for further testing. These tests can help to determine whether the bacteria are a good fit for the treatment plan.
A CT scan can also be used to detect underlying problems in the urinary tract. This test can also reveal if stones are present. The doctor may also order ultrasounds to look for any obstructions in the urinary tract. If the doctor is unsure about the diagnosis, a dimercaptosuccinic acid test may be performed. This test involves the injection of a special material into the body through a vein. The material contains radioactive material that will show the extent of the infection. This test is the gold standard for diagnosing pyelonephritis.
Urine tests may also be performed to determine the presence of blood in the urine. Blood can also be seen on the surface of the kidney. If blood is present, it indicates a more serious infection. In addition, blood may show white blood cell casts, nitrite, leukocyte esterase, or a combination of these substances. If the test shows these symptoms, a doctor may recommend that the patient go to the hospital. If the kidney infection is severe, hospitalization may be the best option.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis may also be seen in pregnant women. This is because of the changes that take place in the body during pregnancy. A pyelonephritis infection can be extremely dangerous to the mother and baby, and it may require hospitalization. If the infection is severe, it may be life-threatening.